Earwigs: Control & Prevention Guide
Earwigs are small, elongated insects known for their distinctive pincers or forceps-like cerci at the end of their abdomen. Belonging to the order Dermaptera, these fascinating creatures are found worldwide in various habitats, with over 2,000 species identified to date. Despite their somewhat menacing appearance, earwigs are mostly harmless to humans, although they can deliver a minor pinch with their cerci when provoked. Earwigs are omnivorous, feeding on a diet that includes plants, insects, and decaying organic matter. They are primarily nocturnal and are characterized by their preference for dark, sheltered hiding places during the day. These insects play a role in natural ecosystems by aiding in decomposition and serving as occasional predators of pests.
The different species of earwig
The most common species of earwig can vary depending on the region and habitat, but some of the well-known and widely distributed species include:
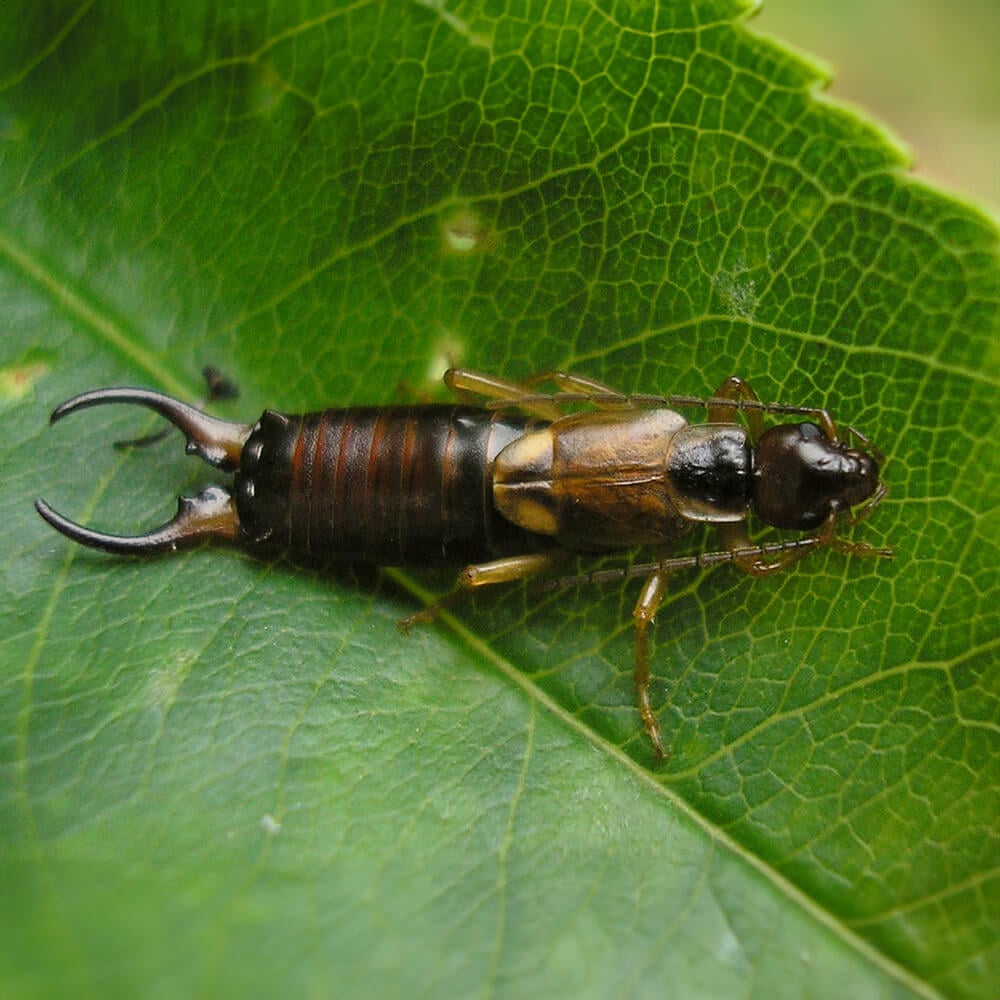

European Earwig (Forficula auricularia)
This is perhaps the most well-known earwig species globally. It is native to Europe but has been introduced to many other parts of the world. It’s often found in gardens and can occasionally become a household pest.
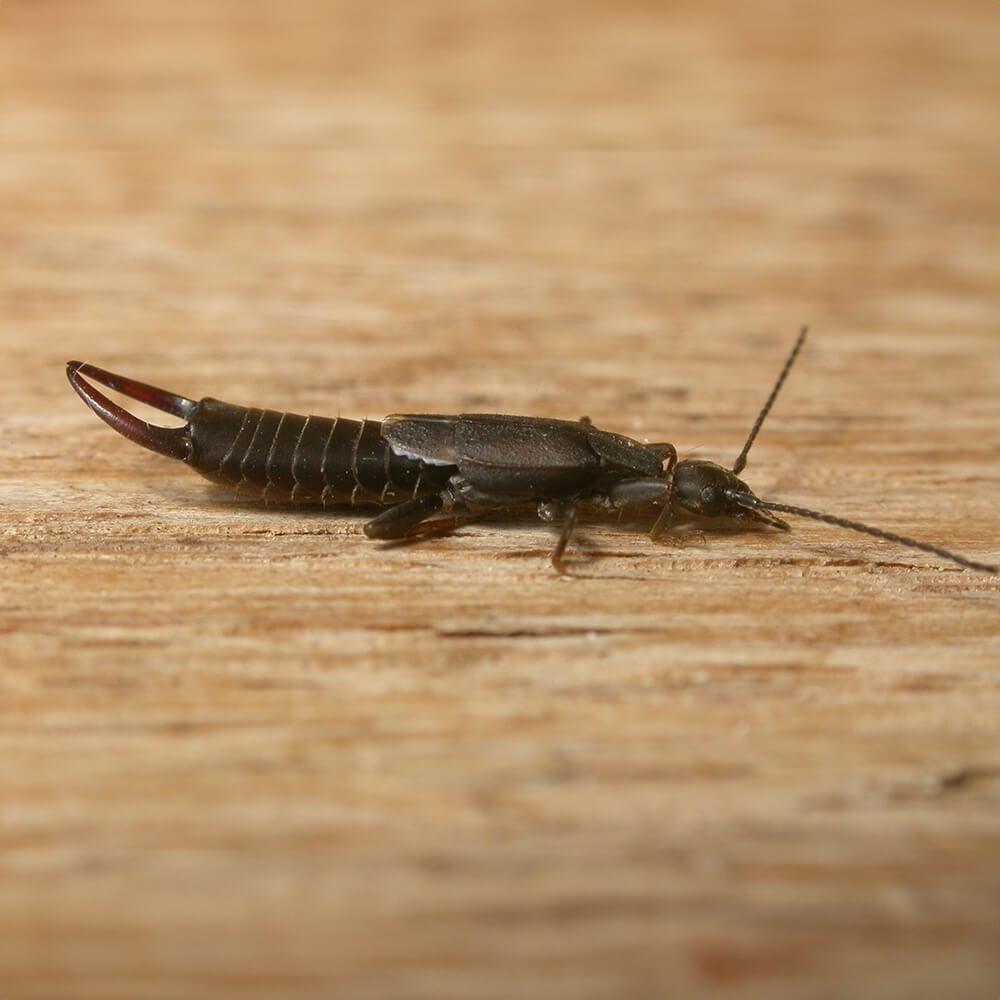

Lesne's Earwig (Labidura lesnei)
Native to Europe, this species is notable for its long and curved forceps. It prefers damp habitats.
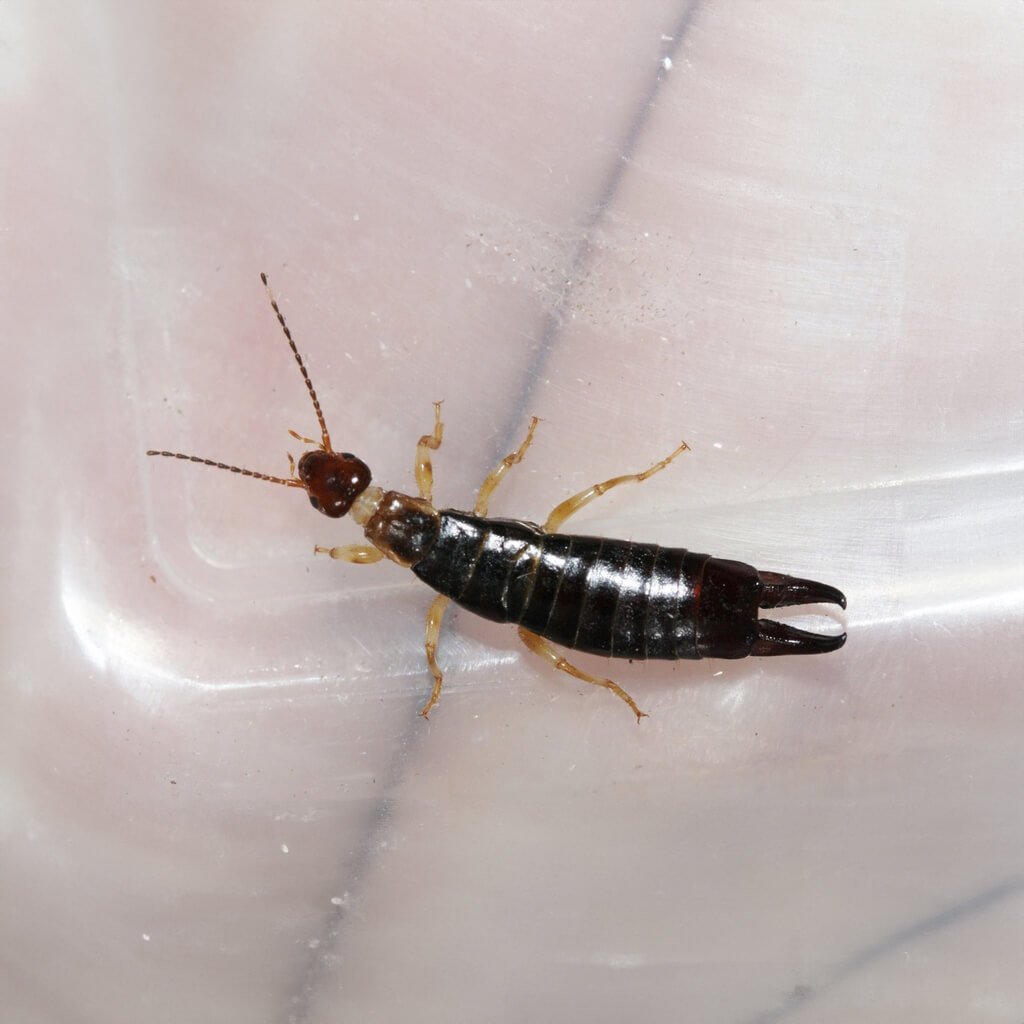

Ringlegged Earwig (Euborellia annulipes)
This species is found in North America and is often encountered in gardens and agricultural fields. They are known for their distinctive banded legs.
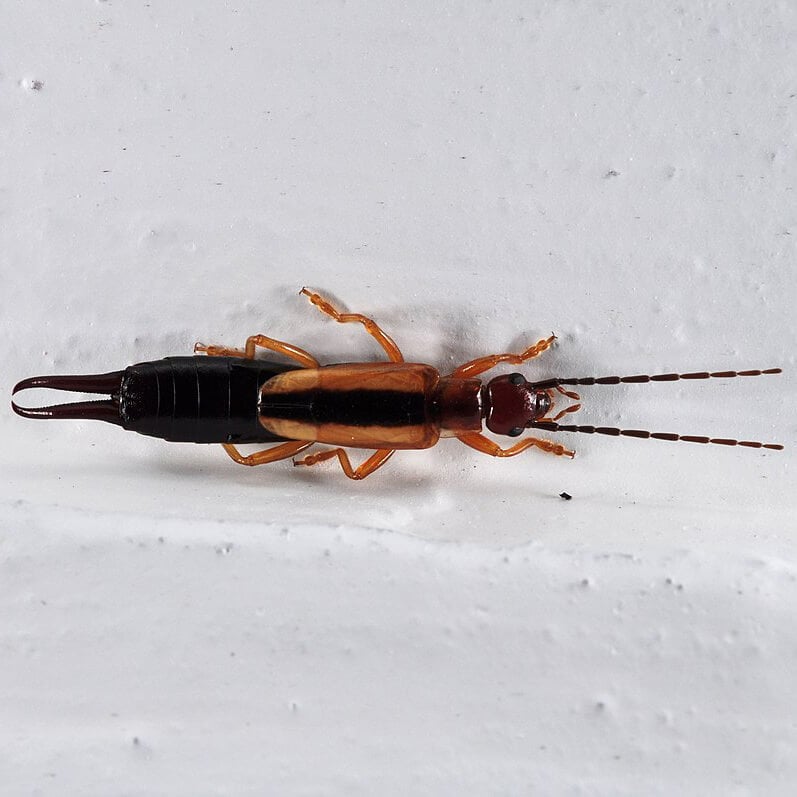

Rove Earwig (Doru taeniatum)
This species is widespread in North America and is commonly found in leaf litter, under rocks, and in other concealed locations.
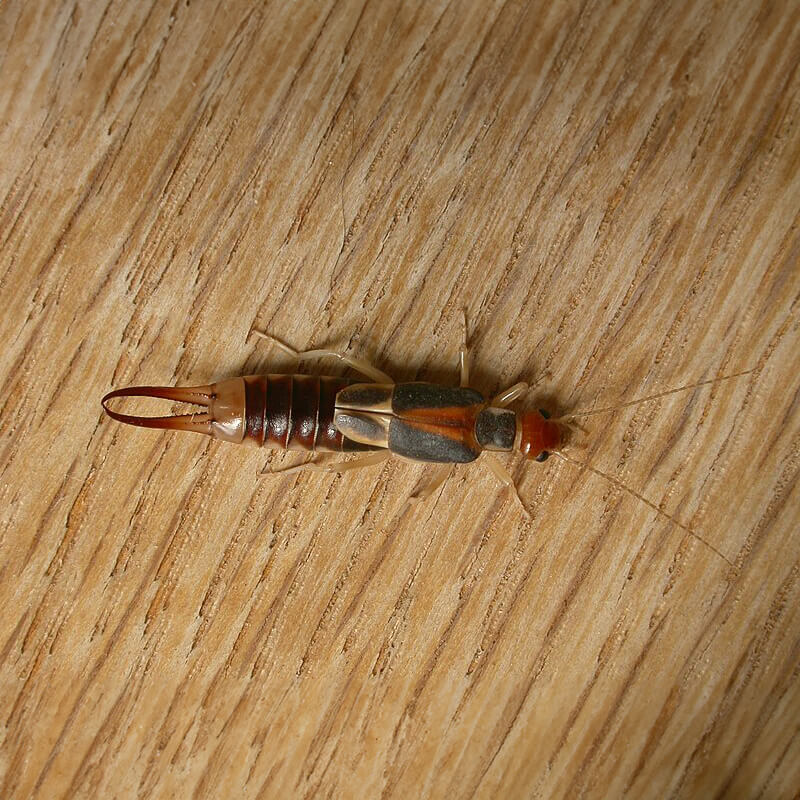

Common Earwig (Labidura riparia)
This species is found in various parts of North America and is particularly common in the southeastern United States. It’s known for its larger size compared to other earwig species.
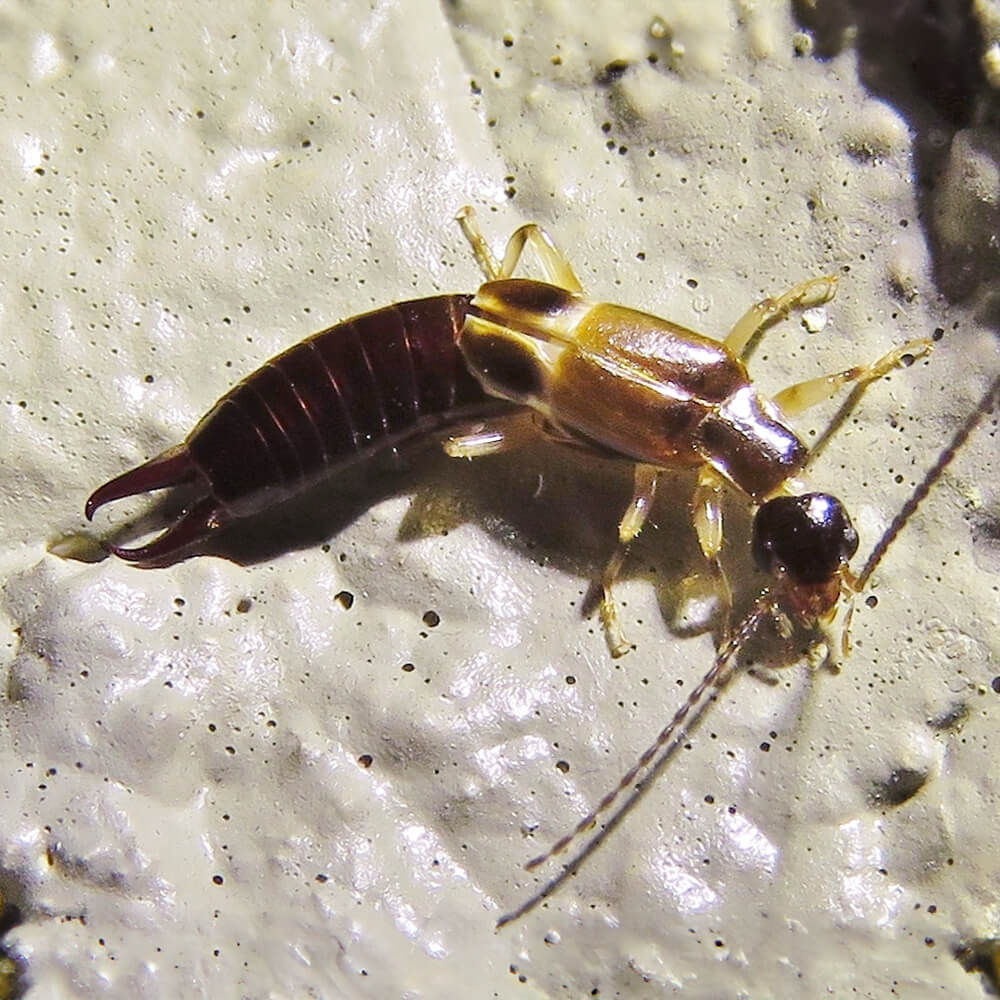

Reddish Earwig (Euborellia cincticollis)
This species is found in various parts of North America and is known for its reddish-brown coloration.
It’s important to note that there are numerous species of earwigs worldwide, and the most common species can vary by location and environmental conditions. While earwigs are often associated with gardens and outdoor environments, some may occasionally find their way into homes as well.
There are over 2,000 species of earwigs found worldwide, with varying sizes and appearances.
The life cycle of earwig
The life cycle of earwigs is a fascinating journey that encompasses several distinct stages, each contributing to their role in the ecosystem. Understanding these phases can shed light on these unique insects’ behavior and biology.

Egg Stage
Earwigs begin their life cycle as eggs, which are typically laid in concealed locations such as underground burrows or beneath plant debris. The female earwig diligently guards her eggs, protecting them from potential threats until they hatch.
Juvenile Stage
As they continue to grow and mature, earwigs enter the juvenile stage. At this point, they resemble adult earwigs in appearance, including the distinctive forceps-like cerci at the tip of their abdomen. They are active and voracious predators, feeding on a variety of prey and plant material.

Reproductive Stage
After mating, female earwigs lay eggs to initiate the next generation, completing the life cycle. The cycle typically repeats itself, with earwigs continuing to contribute to their ecosystem by playing roles as both predators and decomposers.

Nymph Stage
Once the eggs hatch, young earwigs, known as nymphs, emerge. During this phase, they are small and pale, resembling miniature versions of adult earwigs. Nymphs undergo several molts, gradually developing their characteristic pincers and dark exoskeletons.

Adult Stage
Earwigs reach adulthood after a series of molts. This is the stage where they become fully sexually mature and engage in mating activities. Interestingly, earwigs are known for their complex courtship rituals, which involve tactile and chemical signals between males and females.
Throughout their life cycle, earwigs serve as valuable components of various ecosystems, helping control insect populations and aiding in the decomposition of organic matter. Understanding their life cycle provides insights into their role in nature and their adaptability to a wide range of habitats.
Female earwigs are known for their maternal instincts. They protect their eggs and nymphs and may even feed their young by regurgitating food.
The seasons most conducive to earwig
The seasons most conducive to earwig activity are primarily spring and summer. These warm-weather months provide the ideal conditions for earwigs to thrive and carry out their life cycle. Here’s a closer look at how these seasons impact earwig behavior:

Spring
As temperatures rise in the spring, earwigs become more active. This is when they emerge from their overwintering shelters, such as leaf litter, soil crevices, or other concealed locations. With the arrival of spring, earwigs seek out food sources, including insects and decaying plant matter. They are particularly drawn to damp environments, making spring rains and increased humidity favorable for their activities.
Summer
Summer is the peak season for earwigs. The warm and humid conditions of this season are highly conducive to their reproduction and foraging. During summer nights, earwigs are most active, feeding on garden pests like aphids and caterpillars. They also engage in mating rituals and lay their eggs in sheltered locations. The abundance of vegetation and insect prey provides ample resources for earwigs to thrive and reproduce.
While spring and summer are the seasons when earwigs are most active, it’s important to note that they can be found year-round in temperate regions. However, their activity may decrease during the fall and winter months when temperatures drop, and they often seek refuge in protected environments to survive the colder conditions. Understanding the seasonal patterns of earwigs can be helpful for pest control and managing their presence in gardens and outdoor spaces.
They are primarily active at night, which is when they forage for food and mate.
Where do earwig come from, their habitat
Earwigs are found in a variety of habitats around the world, and their natural distribution can vary depending on the species. Here’s an overview of where earwigs come from and their typical habitats:
Origin and Distribution: Earwigs belong to the order Dermaptera, and different species can be found on nearly every continent except Antarctica. The diversity of earwigs is particularly extensive in tropical and subtropical regions. Some species are native to specific continents, while others have been introduced to new areas through human activity.
Habitats: Earwigs are highly adaptable insects and can be found in a wide range of habitats, including:

Gardens and Landscapes
Earwigs are often encountered in gardens, flowerbeds, and agricultural fields. They can be both beneficial and harmful, as they prey on garden pests but may also feed on plant material.

Under Rocks and Logs
Earwigs are nocturnal insects that hide during the day. They frequently seek refuge under rocks, logs, and other debris, making these locations ideal habitats.

Forests
Certain earwig species inhabit forested areas, where they play roles in decomposing organic matter and preying on insects within the leaf litter.

Moist Environments
Many earwig species are associated with damp or moist environments. They are often found in soil, leaf litter, and decaying wood, where they can find shelter and moisture.

Urban Areas
Some earwig species have adapted to urban environments and can be found in and around buildings, particularly in areas with suitable hiding places and food sources.

Caves
In some regions, earwigs have been discovered in cave ecosystems, where they are adapted to the unique conditions found in these dark and humid environments.
It’s important to note that the specific habitat preferences of earwigs can vary by species. While some are more closely associated with natural environments, others have adapted to human-altered landscapes. Understanding their habitat preferences can be valuable for pest management and conservation efforts, as well as for appreciating their ecological roles.
The name “earwig” comes from the old myth that these insects crawl into people’s ears and lay eggs. In reality, this rarely happens.
What attracts earwig into our homes
Understanding what attracts earwigs into our homes can help homeowners take preventive measures to reduce their presence indoors. Earwigs may enter homes for various reasons, and several factors can attract them:
Shelter
Earwigs are nocturnal insects that seek dark and sheltered locations during the day to hide from predators and harsh weather conditions. Homes provide ideal hiding spots, especially in cracks and crevices around the foundation, walls, and doors.
Vegetation
If a home has dense vegetation, such as shrubs or overgrown plants, near its exterior, it can create a bridge for earwigs to move from the garden or yard into the house.
Seasonal Migration
Earwigs may enter homes more frequently during certain seasons, such as fall or winter, when they seek shelter from cold temperatures.
Moisture
Earwigs are drawn to moisture, so any areas of the home with high humidity levels can be attractive to them. Leaky pipes, damp basements, and poorly ventilated areas can create suitable conditions for earwigs.
Food Sources
Earwigs are omnivorous and will feed on a variety of organic matter, including insects, plant material, and decaying organic material. If there are food sources like crumbs or other organic debris inside the home, it can attract earwigs.
Outdoor Lighting
Earwigs are attracted to light sources, including outdoor lights or porch lights. These lights can draw them toward the exterior of a home, and if there are entry points, they may find their way inside.
Cracks and Gaps
Earwigs are small insects and can enter homes through tiny cracks, gaps, and openings around windows, doors, and foundations. Ensuring your home is well-sealed can help prevent their entry.
To prevent earwigs from entering your home, consider the following steps:
-
- Seal cracks and gaps in the home’s exterior.
- Repair any leaks or moisture issues.
- Reduce outdoor lighting near entrances.
- Trim vegetation away from the home.
- Keep the indoor environment clean and free of food debris.
- Use door sweeps and weatherstripping to seal gaps around doors.
- Consider professional pest control services if the infestation is severe.
By addressing these factors and implementing preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of earwigs finding their way into your home.
Earwigs are opportunistic feeders and will eat a variety of foods, including plants, decaying matter, other insects, and even some small animals.
Signs that you have a earwig’ infestation
Recognizing the signs of an earwig infestation is crucial for taking prompt action to address the issue. While earwigs are not typically harmful to humans, they can become a nuisance, especially when their population grows. Here are common signs that you may have an earwig infestation:
Sightings
The most obvious sign of an earwig infestation is the presence of earwigs themselves. You may see them crawling in and around your home, particularly during the evening when they are most active.
Indoor Presence
Earwigs can find their way indoors, particularly in damp and dark areas. If you notice them inside your home, especially in bathrooms, basements, or kitchens, it may indicate an infestation.
Musty Odor
Some people report a musty or unpleasant odor when earwigs are present in large numbers. This odor may be more noticeable in enclosed spaces.
Damage to Plants
Earwigs are known to feed on plant material, and an infestation can lead to damage to your garden or indoor plants. Look for irregular holes and chewed edges on leaves and flowers.
Sheltered Hiding Places
Earwigs seek shelter during the day and may congregate in sheltered spots such as cracks, crevices, and dark corners. Check areas like window sills, door frames, and the spaces around baseboards for their presence.
Mating Rituals
During mating season, male earwigs may engage in their distinctive courtship displays, which can include physical interactions and the release of pheromones. Observing these behaviors can indicate a breeding population.
Damaged Fruits and Vegetables
In gardens or orchards, earwigs may target ripe fruits and vegetables, leaving behind bite marks or partially eaten produce.
Shed Exoskeletons
Like many insects, earwigs shed their exoskeletons as they grow. Finding discarded exoskeletons in and around your home is a sign that earwigs are active.
Nesting Sites
Earwigs may build nests in concealed locations, such as under debris, mulch, or in the soil. Check these areas for signs of earwig nesting activity.
If you suspect an earwig infestation, it’s important to address it promptly to prevent their numbers from increasing. While earwigs are generally harmless to humans, their presence can be a nuisance and lead to damage in gardens or homes. Integrated pest management strategies, such as reducing moisture sources, sealing entry points, and using traps, can help control an earwig infestation effectively. If the problem persists or worsens, consider seeking professional pest control assistance.
When threatened, some earwig species can emit a foul-smelling, yellowish liquid from their abdominal glands as a defense mechanism.
Rooms where earwig hide
Earwigs are nocturnal insects that seek dark and sheltered places to hide during the day. While they may hide in various parts of a home, they tend to prefer areas that provide both darkness and moisture. Here are common rooms and spaces where earwigs are likely to hide indoors:
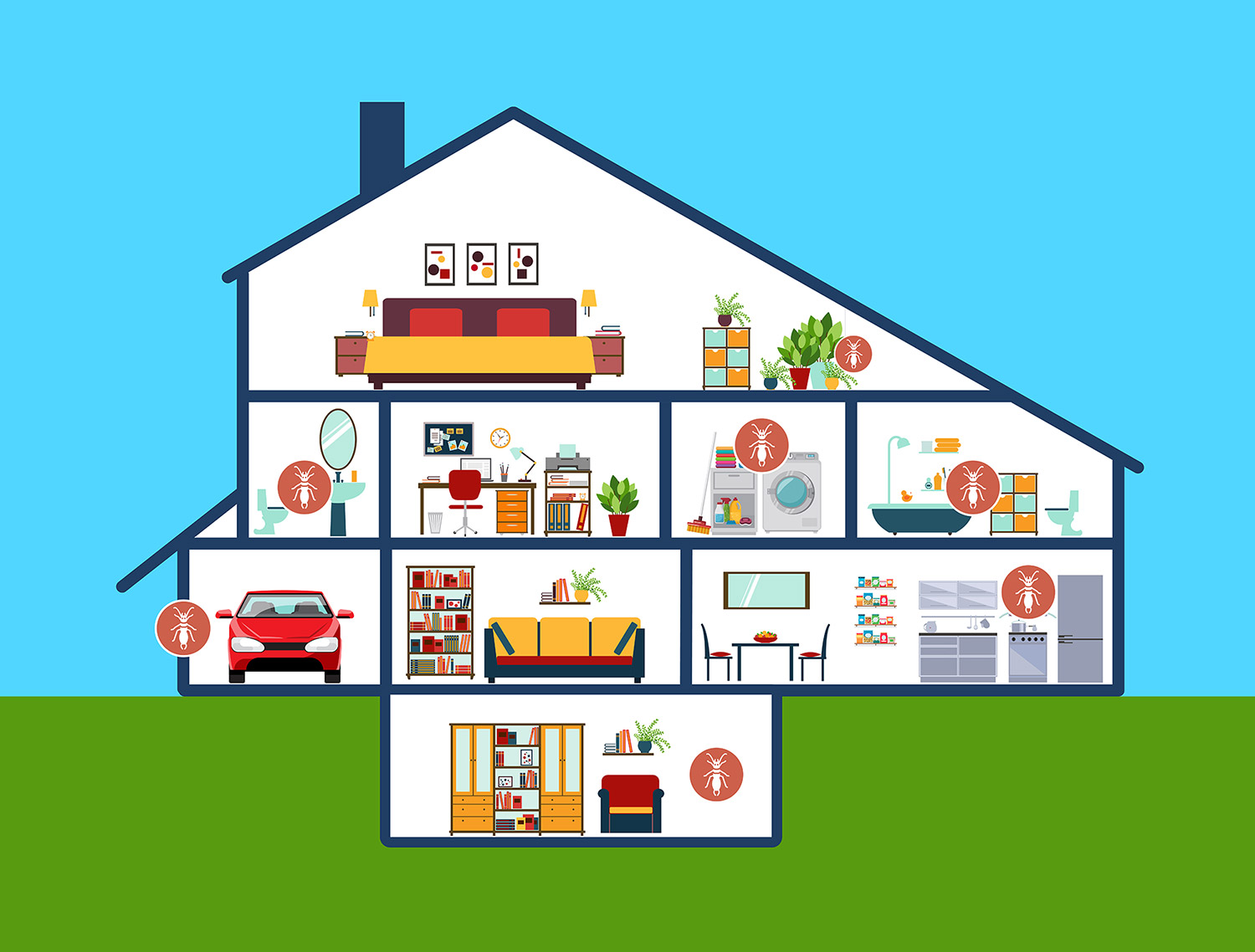
Bathrooms
Bathrooms are attractive to earwigs due to their high humidity levels. Earwigs may hide in damp corners, under sinks, around plumbing fixtures, and behind bathroom cabinets.
Laundry Rooms
Laundry rooms are another area where earwigs may seek moisture. Look for them near washing machines, dryer vents, and floor drains.
Garage
Garages may have ideal hiding spots for earwigs, including under stored items, in corners, and along garage door frames.
Basements
Basements are often cool and dark, making them an ideal hiding spot for earwigs. They may hide in cracks in the walls or floors, along baseboards, and in boxes or stored items.
Crawl Spaces
If your home has a crawl space, earwigs can find their way into these dark, damp areas. They may hide in insulation, under the house, or in cracks and crevices.
Indoor Plants
Earwigs may seek shelter in potted plants or containers, especially if the soil is consistently damp.
Kitchens
Kitchens can provide both moisture and food sources for earwigs. Check under sinks, around dishwashers, and near appliances for their presence. They may also hide in cabinets, especially if there are water leaks or spills.
Utility Rooms
Rooms housing utilities such as water heaters or furnaces can provide shelter for earwigs. Inspect these areas for their presence, especially if there are water leaks.
Cabinets and Drawers
In some cases, earwigs may find their way into cabinets and drawers, particularly if they are near moisture sources like sinks.
It’s essential to identify their hiding places to effectively address an earwig infestation. Reducing moisture sources, sealing entry points, and using traps in these areas can help control their presence. Keep in mind that while earwigs may hide in these spaces, they are generally not harmful to humans and are primarily a nuisance pest.
Earwigs are known for their distinctive pincer-like appendages at the rear end of their bodies, called cerci. These cerci are used for defense, mating, and capturing prey.
The dangers and damages that earwig can cause
Earwigs are generally considered nuisance pests rather than dangerous ones, and they do not pose significant health risks to humans. However, they can cause some minor issues and damage in certain situations. Here are the potential dangers and damages associated with earwigs:
Plant Damage
Earwigs are omnivorous insects that feed on a variety of organic materials, including plants. In gardens and agricultural settings, they can chew on leaves, flowers, fruits, and vegetables, potentially causing cosmetic damage to plants.
Predation on Beneficial Insects
While earwigs primarily consume decaying plant matter and soft-bodied insects, they may also prey on beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which can disrupt natural pest control in gardens.
Pinching
Earwigs have pincers or forceps-like cerci at the end of their abdomen, which they use for defense. While these pincers can deliver a pinch, it is generally mild and rarely causes harm to humans. However, it can be uncomfortable if an earwig pinches someone.
Feeding on Seedlings
Young seedlings and newly planted garden crops can be vulnerable to earwig feeding. Earwigs may consume the tender shoots, potentially hindering plant growth.
Occasional Home Invasions
Earwigs can find their way into homes seeking shelter, especially in damp or humid conditions. While they do not transmit diseases or cause structural damage, their presence indoors can be unsettling for some people.
It’s important to note that the vast majority of earwig species are harmless to humans and are more beneficial than harmful in natural ecosystems. They play roles in decomposing organic matter and can help control certain garden pests. If you encounter earwigs in your home or garden and their presence becomes problematic, it is recommended to implement integrated pest management strategies to manage their numbers effectively. This may include reducing moisture sources, sealing entry points, and using traps rather than resorting to chemical pesticides, which can have unintended environmental consequences.
While earwigs can sometimes damage plants, they are also beneficial in gardens as they eat various pests like aphids, mites, and small insects.
How to get rid of earwig / Available treatments
Getting rid of earwigs can be accomplished through a combination of preventive measures and treatment options. Here are steps you can take to control and eliminate earwig infestations:
Reduce Moisture Sources
- Fix any leaks or water issues in and around your home.
- Ensure proper drainage away from your house’s foundation.
- Remove standing water from containers or low-lying areas.
Use Physical Barriers
- Place sticky traps or adhesive tape in areas where earwigs are active, such as near hiding spots and entry points.
- Create a barrier of diatomaceous earth or crushed eggshells around vulnerable plants in your garden.
Insecticides
- As a last resort, consider using insecticides labeled for earwig control. Apply them in and around hiding spots, entry points, or infested areas.
- Follow the instructions on the product label carefully and use pesticides with caution, as they may have environmental impacts and should be a last resort.
Seal Entry Points
- Seal cracks, gaps, and openings in your home’s exterior using caulk or weatherstripping.
- Install door sweeps to prevent earwigs from entering through gaps beneath doors.
Nighttime Collection
- Go out at night when earwigs are active and use a flashlight to collect them manually.
- Wear gloves to protect your hands.
Professional Pest Control
- If your earwig infestation persists or is severe, consider hiring a professional pest control service. They can assess the situation and use targeted treatments to eliminate the problem.
Outdoor Cleanup
- Remove piles of leaves, mulch, and other organic debris near your home’s foundation.
- Trim back vegetation and keep plants away from the house.
- Elevate firewood and stacked materials off the ground.
Natural Predators
- Encourage natural predators of earwigs, such as birds, toads, and ground beetles, to inhabit your garden.
Remember that the use of chemical pesticides should be a last resort, as it can have unintended consequences for other beneficial insects and the environment. Integrated pest management, which combines multiple strategies, is often the most effective and environmentally friendly approach to control earwigs. By implementing these methods, you can significantly reduce earwig populations and minimize their impact on your home and garden.
Earwigs typically live for about one year, with some species having shorter or longer lifespans.
How to prevent earwig infestations
Preventing earwig infestations is essential to minimize their presence in and around your home. By taking proactive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of an earwig problem. Here are steps to help prevent earwig infestations:
Reduce Moisture
- Fix leaks in plumbing and gutters.
- Ensure proper drainage away from your home’s foundation.
- Avoid overwatering outdoor plants and lawns.
Create Barriers
- Place a barrier of diatomaceous earth or crushed eggshells around plants in your garden to deter earwigs.
- Use sticky traps near plants or hiding spots to capture wandering earwigs.
Predators
Encourage natural predators of earwigs, such as birds, toads, and ground beetles, to inhabit your garden by providing appropriate habitats and food sources.
Regular Cleaning
Keep your home clean and free of crumbs, food debris, and spills, as this can help prevent indoor earwig sightings.
Seal Entry Points
- Use caulk or weatherstripping to seal gaps around doors and windows.
- Install door sweeps to block gaps beneath exterior doors.
- Repair damaged screens on doors and windows.
Nighttime Inspection
Since earwigs are nocturnal, inspect your yard and garden at night with a flashlight to identify and manually remove earwigs.
Keep Indoor Areas Dry
In humid areas like bathrooms, use exhaust fans or dehumidifiers to reduce moisture levels.
Outdoor Maintenance
- Keep your yard and garden well-maintained. Regularly clean up organic debris like fallen leaves and mulch.
- Trim back vegetation, especially plants that touch your home’s exterior.
- Elevate firewood and stacked materials off the ground to deter earwigs from nesting.
Reduce Outdoor Lighting
Earwigs are attracted to light sources. Consider using outdoor lighting less or switch to yellow or sodium vapor bulbs, which are less attractive to insects.
Store Food Securely
In kitchens, store food in airtight containers to eliminate potential food sources for earwigs.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can make your property less attractive to earwigs and reduce the chances of an infestation. Integrated pest management, which combines several of these strategies, is an effective way to maintain a pest-free environment while minimizing environmental impacts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while earwig infestations are generally more of a nuisance than a serious threat, they can still disrupt our homes and gardens. Earwigs seek shelter in dark, damp places, and their presence may be more noticeable during periods of increased moisture or when seeking refuge from harsh weather conditions. Although they are known for their distinctive pincers, earwigs are not typically harmful to humans.
Preventing and managing earwig infestations can be effectively achieved through a combination of proactive measures, such as reducing moisture sources, sealing entry points, and implementing natural control methods. Chemical pesticides should be a last resort due to potential environmental impacts.
Understanding the behavior, habitats, and potential damages associated with earwigs allows us to take informed actions to minimize their presence and maintain a harmonious coexistence with these ancient insects. By striking a balance between effective pest management and ecological preservation, we can ensure a healthier and more comfortable living environment for ourselves and the natural world.
