Effective Bed Bug Solutions
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are pesky insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. These tiny, reddish-brown pests are a common household nuisance, often found in mattresses, furniture, and cracks and crevices. While their bites are not known to transmit diseases, they can cause itchy, red welts on the skin, leading to discomfort and sleep disturbances. Early detection is vital for effective bed bug control, as they reproduce quickly and can be challenging to eradicate once they infest a space.
The different species of bed bugs
Bed bugs are small, blood-feeding insects that belong to several distinct species, each with its own unique characteristics and habits. Understanding these different species is essential for effective pest control and prevention.
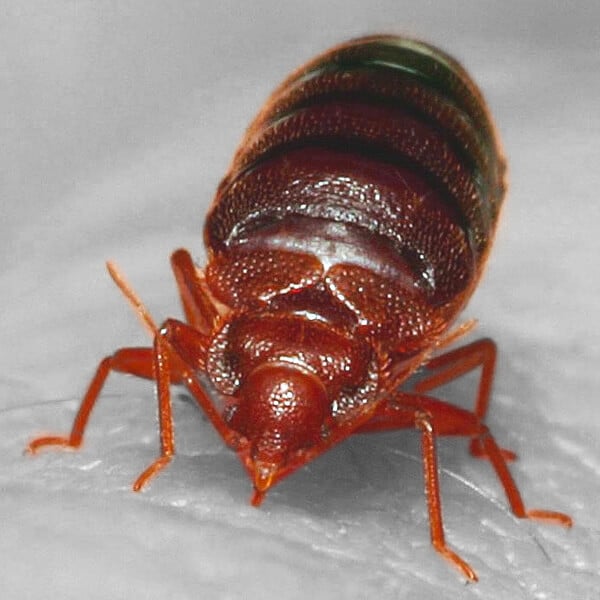

Cimex lectularius (Common Bed Bug)
The common bed bug, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, is the species most often associated with infestations in human dwellings. These reddish-brown, oval-shaped insects are skilled hitchhikers, often traveling on luggage or clothing. They hide in cracks and crevices during the day, emerging at night to feed on the blood of their sleeping hosts. Identifying common bed bugs is crucial for timely intervention and effective treatment.
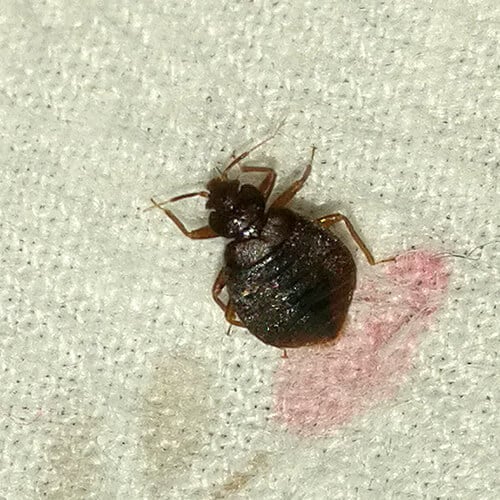

Leptocimex boueti (Bat Bug)
Leptocimex boueti, also known as the bat bug, primarily feeds on the blood of bats but can bite humans if their primary host is unavailable. These bugs share a close resemblance to common bed bugs, making identification challenging without expert knowledge. Effective pest management requires accurate differentiation between bat bugs and their human-oriented counterparts.
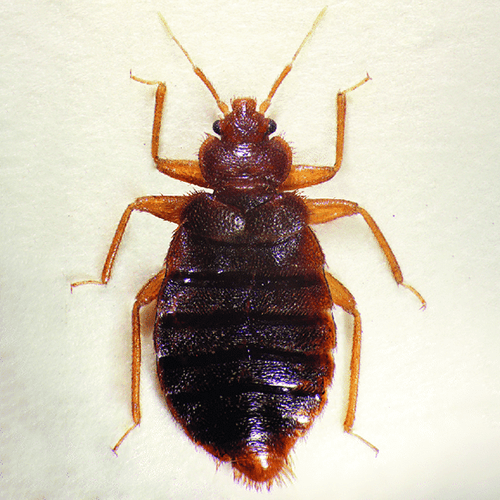

Cimex hemipterus (Tropical Bed Bug)
Cimex hemipterus, commonly referred to as the tropical bed bug, is another blood-feeding species closely related to the common bed bug. As the name suggests, they are often found in tropical and subtropical regions. While their appearance and habits are similar to Cimex lectularius, distinguishing between the two species is vital for targeted control measures.
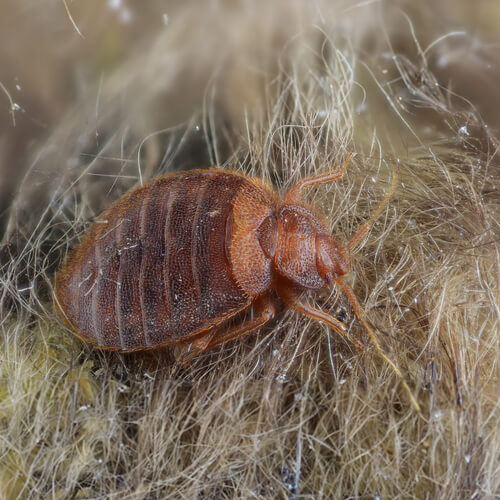

Cimex adjunctus (Eastern Bat Bug)
Cimex adjunctus, or the eastern bat bug, is another species closely related to bed bugs. They, too, primarily feed on bats but can occasionally bite humans. These bugs are often found in regions where bats roost, and their presence can indicate a bat infestation in a building. Proper identification of this species aids in addressing both the bat and bug problems.
Understanding the various ant species is not only intriguing but also valuable for pest control, conservation efforts, and ecological studies. Each species contributes uniquely to the balance of ecosystems, making ants a vital part of our natural world.
Adult bed bugs are tiny, typically measuring only about 4-5 millimeters in length. Despite their small size, they are known for their resilience and ability to survive without feeding for several months.
The life cycle of bed bugs
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs is essential for effective pest management and prevention. Bed bugs undergo a series of developmental stages, each with distinct characteristics.

Egg Stage
The life cycle of a bed bug begins with the egg stage. Female bed bugs lay tiny, translucent eggs in hidden locations, such as mattress seams, cracks, and crevices. These oval-shaped eggs are approximately 1mm long and can be challenging to spot with the naked eye. In optimal conditions, bed bug eggs hatch in about 6 to 10 days.

Reproduction
Bed bugs reproduce through a process known as traumatic insemination, where males puncture the female’s abdomen to inseminate her. After mating, females lay eggs in hidden locations, typically within cracks and crevices near their resting places. A single female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs during her lifetime, contributing to the rapid population growth of an infestation.
Nymph Stage
Once hatched, bed bug nymphs emerge as miniatures of adult bed bugs, albeit smaller and lighter in color. Nymphs go through several developmental instars, or stages, where they shed their exoskeletons to grow. Each instar requires a blood meal to progress to the next stage. Nymphs closely resemble adult bed bugs but lack wings and are often pale or translucent.

Adult Stage
After completing their nymphal stages, bed bugs reach adulthood. Adult bed bugs are about 4 to 5mm in length and have a reddish-brown coloration. They are oval-shaped and wingless, with six legs and a flattened body. Adult bed bugs require regular blood meals to reproduce, and they are most active at night when they feed on sleeping hosts. Under optimal conditions, bed bugs can live several months to over a year as adults.
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs is crucial for effective pest control efforts. Identifying bed bug eggs, nymphs, and adults is essential for timely intervention and the implementation of targeted treatment strategies. If you suspect a bed bug infestation in your home or business, it is advisable to consult a professional pest control service with expertise in managing these persistent pests throughout their life cycle.
Bed bugs are nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active at night. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by sleeping hosts, making beds and sleeping areas their primary feeding grounds.
The seasons most conducive to bed bugs
Bed bugs are notorious for their adaptability and resilience, thriving in various environments. However, certain seasons provide more favorable conditions for their infestations to flourish. Understanding when bed bugs are most active can help you take preventive measures and identify potential infestations. In this informative article, we’ll delve into the seasons that are most conducive to bed bugs and provide insights into their behavior during each season.

Spring
Spring is a season when bed bug activity tends to increase. As temperatures rise, bed bugs become more active, seeking blood meals more frequently. This season’s warmer and more humid conditions provide an ideal environment for bed bugs to thrive and reproduce. Additionally, spring often marks the end of hibernation for outdoor pests, increasing the risk of infestations being introduced into homes and businesses.

Fall
As summer transitions into fall, bed bugs continue to be active, although their activity may start to decline as temperatures gradually decrease. However, fall is when bed bugs often seek shelter indoors to escape the cooling weather. This migration indoors can lead to an uptick in infestations as they settle into cracks, crevices, and bedding.
Summer
Summer is considered the peak season for bed bug infestations. The warm and humid weather accelerates their reproductive cycle, leading to a rapid increase in their numbers. During this season, bed bugs are highly active and can be found in various areas of a dwelling, including bedrooms, living rooms, and even offices. Increased travel and social activities can also contribute to the spread of bed bugs during the summer months.
Winter
Winter is the least conducive season for bed bugs. These pests become less active in cold temperatures and may enter a state of dormancy, slowing down their reproductive cycle. While bed bug activity decreases during winter, it doesn’t mean they disappear entirely. Infestations can still persist, especially in well-heated indoor environments where bed bugs can remain active throughout the year.
While bed bugs can be a year-round problem, their activity tends to peak during the warmer seasons, particularly in spring and summer. Vigilance and preventive measures are crucial during these times to minimize the risk of infestations. If you suspect a bed bug issue in your home or business, consider seeking professional pest control services to address the problem effectively, regardless of the season.
Bed bugs are adaptable pests that aren’t tied to specific seasons. They’re more active in warmer months, reproducing faster, while in winter, they become less active, making infestations harder to detect.
Where do bed bugs come from, their habitat
Understanding where bed bugs originate and their preferred habitats is crucial for effective prevention and management. These resilient pests can be introduced from various sources, and knowing their hiding places can help detect and address infestations early.
Origin and Introduction
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, have a long history of infesting human dwellings. While their exact origin is unclear, they are believed to have evolved from bat bugs that initially fed on bats. Over time, they adapted to feed on humans and other mammals. Bed bugs are thought to have spread worldwide through human migration, trade, and travel.
Preferred Habitats

Bedrooms and Mattresses
Bed bugs are famously associated with beds and mattresses, where they hide in seams, folds, and crevices. These nocturnal insects emerge at night to feed on their sleeping hosts, leaving itchy bite marks.

Luggage and Travel Gear
Travel is a common way bed bugs are introduced into homes. They can hitch a ride in luggage, clothing, or personal items from infested hotels or transportation.
Public Spaces
Bed bugs can also be found in public spaces, such as libraries, theaters, and public transportation, where they may hide in seating or cracks in furniture.
Furniture and Upholstery
Bed bugs can infest upholstered furniture, such as sofas and chairs. They hide in the seams and cushions, making them difficult to detect.

Clothing and Personal Items
Bed bugs may infest clothing, especially when it’s left on infested furniture or in cluttered areas.
Cracks and Crevices
Bed bugs are skilled at finding tiny hiding spots in walls, baseboards, and electrical outlets. They use these hidden locations as harborage during the day, emerging at night to feed.

Multi-Unit Dwellings
Apartments, condominiums, and shared housing are at higher risk of bed bug infestations due to their ability to move between units through walls and plumbing.
Bed bugs are versatile pests that can be introduced from various sources and thrive in a wide range of environments. Understanding their preferred habitats and sources of introduction is essential for early detection and effective pest control. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, it’s crucial to consult with a professional pest control service to identify the source and implement targeted treatment strategies.
Bed bugs are highly adaptable and can thrive in various habitats. They commonly infest human dwellings but can also be found in places like hotels, theaters, and public transportation. Their ability to adapt to different environments makes them challenging to eradicate.
What attracts bed bugs into our homes
Knowing what attracts bed bugs into our homes is essential for effective prevention and early detection. These resilient pests have a keen sense for certain environmental cues and human behaviors that make your living space more enticing.
Human Presence
Bed bugs are attracted to the carbon dioxide, warmth, and body heat emitted by humans and animals. When you’re in your home, your mere presence can draw them out of their hiding places, especially when you’re at rest during sleep. This is when they are most likely to feed.
Travel and Commuting
Traveling or using public transportation can expose you to bed bugs. They can hide in luggage, backpacks, and clothing and be inadvertently brought back into your home after staying in infested accommodations or sitting in infested public spaces.
Scent and Chemical Attractants
Bed bugs are attracted to certain scents, such as pheromones released by other bed bugs. Additionally, they can be drawn by the scent of sweat or body odor, which may linger on bedding and clothing.
Clutter and Hiding Spots
Bed bugs thrive in cluttered environments where they can find numerous hiding spots. Excess clutter provides more places for them to harbor during the day, making it more challenging to detect and eliminate infestations.
Shared Spaces
Living in multi-unit dwellings or sharing common laundry facilities increases the risk of bed bug infestations. Bed bugs can easily move between units through walls and plumbing, making it crucial to take precautions in such environments.
Infested Items
Bringing infested items into your home is a direct way to attract bed bugs. Used furniture, clothing, luggage, or even items from a friend’s infested home can carry hitchhiking bed bugs. Always inspect secondhand items thoroughly before bringing them indoors.
Pets
Although bed bugs prefer to feed on humans, they may also bite pets if humans are not available. Pet bedding and sleeping areas can become infested, leading to discomfort for both pets and their owners.
Understanding what attracts bed bugs into your home is the first step in preventing infestations. By minimizing clutter, inspecting used items, and practicing good hygiene, you can reduce the risk of attracting these pests. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, it’s crucial to seek professional pest control services for proper identification and targeted treatment.
Bed bugs are attracted to the scent of carbon dioxide, body odor, and other chemical odors produced by humans. They use these cues to locate their hosts for feeding.
Signs that you have a bed bugs’ infestation
Early detection of a bed bug infestation is essential for prompt and effective pest control. Being able to identify the signs of bed bug presence can save you from the discomfort and inconvenience they bring.
Visible Bed Bugs
One of the most direct signs of a bed bug infestation is the presence of the bugs themselves. Adult bed bugs are small, reddish-brown, and about the size of an apple seed. Nymphs (young bed bugs) are smaller and lighter in color. You may find them hiding in seams, folds, or crevices of mattresses, furniture, or walls.
Sweet, Musty Odor
Some people describe the odor of a bed bug infestation as sweet and musty. While not everyone can detect this scent, it may be present in heavily infested areas. The odor is produced by the bugs’ scent glands.
Aggregations of Bugs
In more severe infestations, you may notice groups or clusters of bed bugs in areas where they congregate, such as seams and creases of mattresses or along baseboards.
Bite Marks on Skin
Bed bug bites can cause itchy, red, and often clustered bite marks on your skin. These bites typically appear on areas of your body that are exposed while sleeping, such as the arms, legs, neck, and face. The appearance of these bites can vary from person to person, but they often form a zigzag pattern or line.
Exoskeletons and Eggs
Bed bugs go through multiple molts as they grow, shedding their exoskeletons (skins). You may find these exoskeletons in areas where bed bugs hide. Additionally, bed bug eggs are small, translucent, and sticky. They are usually found in clusters and may be attached to surfaces near their hiding spots.
Tiny Bloodstains on Bedding
Bed bugs feed on blood, and after feeding, they may leave behind small, rust-colored stains on sheets, pillowcases, and mattresses. These stains are a result of their excrement, and they can be an indicator of bed bug activity.
Fecal Droppings
Bed bugs excrete dark, tiny fecal droppings that resemble black or brown specks. These droppings can often be found on bedding, furniture, or near their harborage sites.
Recognizing the signs of a bed bug infestation is crucial for timely intervention. If you suspect you have a bed bug problem, it’s advisable to consult a professional pest control service for a thorough inspection and targeted treatment. Early detection and action can help prevent the infestation from spreading and causing further discomfort.
Over the years, bed bugs have developed resistance to many common pesticides, making their control and elimination more challenging. Pest control professionals often employ a variety of strategies and treatments to manage infestations.
Rooms where bed bugs hide
Understanding the hiding spots of bed bugs is crucial when it comes to preventing and dealing with infestations. These nocturnal pests are masters at concealment, and knowing where to look can make a significant difference in keeping your home bed bug-free.
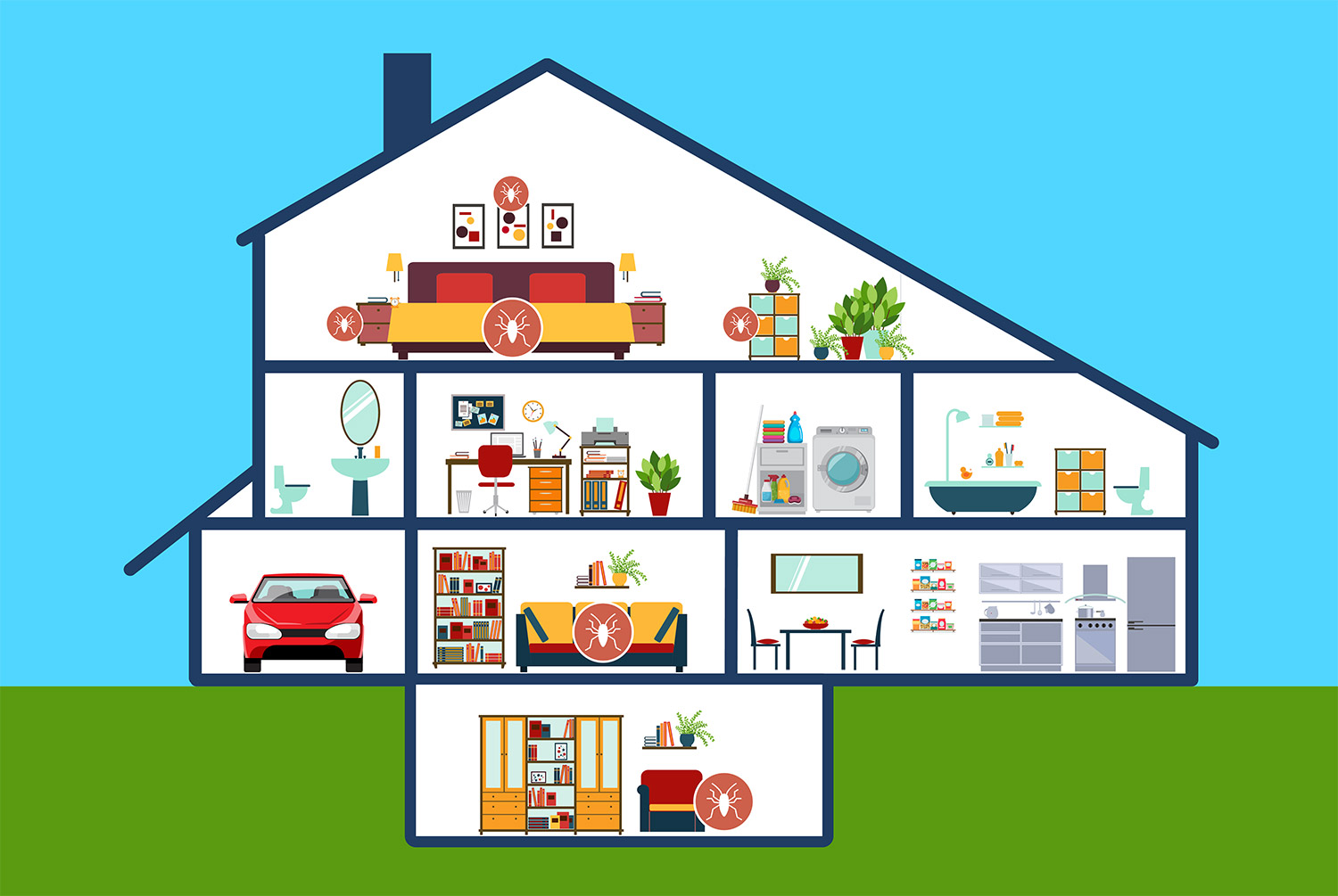

Mattresses and Box Springs
Bed bugs are notorious for hiding in and around mattresses and box springs. They often find refuge in the seams, folds, and crevices of these items. Regularly inspect your bedding for any signs of these unwelcome guests.
Cracks and Crevices
Bed bugs are skilled at squeezing into tiny cracks and crevices in walls, baseboards, and flooring. Seal any gaps and cracks to reduce potential hiding places
Nightstands and Dressers
Bed bugs may hide in the drawers of nightstands and dressers, as well as behind or underneath these pieces of furniture.
Wall Decorations
Wall hangings, picture frames, and mirrors can also hide bed bugs behind or within them. Inspect these items periodically.
Bed Frames
Bed bugs can also infest the frame of your bed. Check joints, cracks, and screw holes for any evidence of bed bug activity.
Electrical Outlets
These pests can even find their way into electrical outlets. While they may not nest there, they can use them as a pathway to other areas of your home. Consider installing outlet covers designed to keep out bed bugs.
Ceilings and Light Fixtures
Although less common, bed bugs can hide on or around ceilings and light fixtures. Check these areas if you suspect an infestation.
Furniture
Upholstered furniture, such as couches and chairs, can provide cozy hiding spots for bed bugs. Inspect the seams, cushions, and seams of your furniture regularly.
Luggage and Clothing
After traveling or staying in an infested location, bed bugs can hitch a ride in your luggage or attach themselves to clothing. Be cautious and inspect your luggage and clothing after a trip.
Carpet and Rugs
Bed bugs can hide in the fibers of carpets and rugs, making it important to regularly vacuum and, if necessary, steam clean these surfaces.
By staying vigilant and inspecting these common hiding spots regularly, you can reduce the risk of a bed bug infestation taking hold in your home. If you suspect you have a bed bug problem, it’s advisable to seek professional pest control services for effective eradication.
Bed bugs are expert hiders, often residing in hidden spots within rooms. They favor cracks, crevices, and seams of mattresses, furniture, and walls. Their ability to hide in plain sight makes them elusive, and they are often only discovered when infestations have become substantial.
The dangers and damages that bed bugs can cause
While bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, they can still pose significant dangers and cause a range of damages. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for prompt action and effective bed bug control.
Health Risks
- Skin Irritation: Bed bug bites can lead to skin irritation, redness, itching, and discomfort. Some individuals may experience severe allergic reactions to the bites, requiring medical attention.
- Secondary Infections: Scratching bed bug bites can break the skin, increasing the risk of secondary bacterial infections. These infections can be painful and may require antibiotics.
- Sleep Disturbances: Bed bugs are nocturnal pests, and their nighttime feeding can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue, stress, and decreased productivity.
Emotional Toll
- Embarrassment and Shame: Many individuals feel embarrassed or ashamed if they have a bed bug infestation, which can impact their self-esteem and mental health.
- Time and Effort: Dealing with a bed bug infestation requires significant time and effort, from cleaning and laundering to coordinating with pest control professionals. This can disrupt daily routines and activities.
Financial Costs
- Pest Control Expenses: Treating a bed bug infestation can be expensive, involving professional pest control services, chemical treatments, and the cost of replacing infested items.
- Property Damage: Bed bugs can damage furniture, mattresses, and other belongings. The need to discard infested items further adds to the financial burden.
Psychological Effects
- Anxiety and Stress: The presence of bed bugs can lead to anxiety and stress due to the constant fear of being bitten. This psychological impact can affect mental well-being and quality of life.
- Social Isolation: People with bed bug infestations may avoid social gatherings and inviting guests over, fearing the stigma associated with these pests.
Spreading Infestations
- Neighborly Relations: Bed bugs can easily spread between units in multi-unit dwellings, leading to disputes and strained relationships among neighbors.
- Wider Community Impact: High-density urban areas and shared transportation can facilitate the spread of bed bugs to various locations, affecting communities at large.
While bed bugs do not transmit diseases, they can cause a range of dangers and damages, both physical and emotional. Recognizing the potential risks associated with bed bug infestations is essential for taking proactive measures to prevent and address these pests promptly. If you suspect a bed bug infestation in your home or business, it’s advisable to consult with professional pest control services to mitigate the dangers and damages caused by these persistent pests.
While bed bugs don’t transmit diseases, their bites can cause itchy, uncomfortable skin reactions in some people. The real danger lies in the emotional and psychological distress they can cause. Bed bug infestations can lead to anxiety, sleep disturbances, and stress, impacting a person’s overall well-being.
How to get rid of bed bugs / Available treatments
Dealing with a bed bug infestation can be challenging, but it’s essential to take prompt and effective action to get rid of these persistent pests.
Professional Pest Control
Engaging a professional pest control service is often the most effective way to eliminate bed bugs. Pest control experts are trained to identify infestations, apply appropriate treatments, and ensure the complete removal of bed bugs. Common professional treatments include:
- Chemical Treatments: Pest control professionals may use insecticides specifically designed to target bed bugs. These treatments are applied to infested areas, cracks, crevices, and hiding spots.
- Heat Treatments: Heat treatments involve raising the temperature of the infested area to a level lethal to bed bugs. This approach is effective in killing bed bugs and their eggs.
- Steam Treatments: High-temperature steam can be used to kill bed bugs and their eggs on contact. Steam treatments are particularly useful for mattresses, furniture, and other infested items.
- Fumigation: Fumigation is a more extensive treatment used in severe infestations. It involves sealing the infested area and introducing a gas that eradicates bed bugs.
DIY Bed Bug Control
While professional pest control is often recommended for severe infestations, some individuals may attempt DIY treatments. These may include:
- Vacuuming: Regular vacuuming of infested areas, along with the immediate disposal of the vacuum bag or contents, can help reduce the bed bug population.
- Washing and Drying: Laundering infested clothing, bedding, and linens in hot water followed by high-temperature drying can kill bed bugs and their eggs.
- Mattress Encasements: Using mattress and box spring encasements can trap bed bugs and prevent them from accessing or escaping from these items.
- Diatomaceous Earth: This natural substance can be sprinkled in cracks and crevices to dehydrate and kill bed bugs. However, it may take time and multiple applications to be effective.
Preventative Measures
Preventing future infestations is essential after treatment. Consider the following preventative measures:
Regular Cleaning: Maintain a clutter-free and clean living space to reduce hiding spots for bed bugs.
- Sealing Cracks and Crevices: Seal gaps in walls, baseboards, and furniture to eliminate hiding places.
- Inspect Secondhand Items: Carefully inspect used furniture and clothing before bringing them into your home.
- Travel Precautions: When traveling, inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs, and keep luggage elevated on racks rather than on the floor.
Eradicating bed bugs requires a combination of treatments, including professional pest control, DIY measures, and preventative actions. The choice of treatment depends on the extent of the infestation and personal preferences. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, consult with a professional pest control service to assess the situation and determine the most appropriate course of action for complete eradication.
Consider regular pest inspections by professionals to detect and address potential ant issues before they become infestations.
How to prevent bed bugs infestations
Preventing bed bug infestations is far easier and less stressful than dealing with a full-blown infestation. These resilient pests can infiltrate even the cleanest of environments, but there are proactive measures you can take to minimize the risk of bed bug problems.
Inspect Secondhand Items
Before bringing used furniture, mattresses, or clothing into your home, carefully inspect them for signs of bed bugs. Look for live bugs, exoskeletons, eggs, and dark fecal stains. If you find any suspicious signs, consider avoiding the item or treating it before introducing it into your living space.
Regular Cleaning
Maintain a clean living space to reduce hiding spots for bed bugs:
- Vacuum Regularly: Vacuum mattresses, furniture, and carpets regularly, paying special attention to seams, folds, and crevices. Dispose of the vacuum bag or clean the vacuum canister promptly.
- Launder Bedding: Wash and dry bedding, curtains, and linens at high temperatures regularly.
- Declutter: Minimize clutter in your living space to reduce hiding spots for bed bugs.
Use Bed Bug-Proof Encasements
Invest in bed bug-proof encasements for mattresses and box springs. These encasements not only trap any existing bed bugs inside but also prevent new infestations.
Monitor for Early Signs
Regularly inspect your sleeping area for signs of bed bugs. Look for bites on your skin, tiny bloodstains on bedding, and fecal spots. Early detection can prevent a small infestation from becoming a larger problem.
Travel Smart
Bed bugs can hitch a ride in luggage and travel gear. When traveling, take these precautions:
- Inspect Hotel Rooms: Upon arrival, check the mattress seams, headboard, and nearby furniture for signs of bed bugs. Store your luggage on luggage racks, not on the floor or bed.
- Use Protective Covers: Consider using bed bug-proof encasements for your luggage and clothing to prevent bed bugs from infiltrating your belongings.
- Inspect After Returning: When you return home from a trip, carefully inspect your luggage and wash your travel clothing immediately in hot water, followed by high-temperature drying.
Seal Cracks and Crevices
Bed bugs often hide in cracks and crevices. Seal gaps in walls, baseboards, and furniture with caulk or sealant to eliminate potential hiding places.
Be Cautious with Used Clothing
When shopping for secondhand clothing, inspect items thoroughly before purchasing. Wash and dry any used clothing at high temperatures before wearing them.
Educate Yourself
Familiarize yourself with the appearance and behavior of bed bugs. Knowing what to look for and being aware of the signs can help you take prompt action if you suspect an infestation.
Preventing bed bug infestations involves a combination of vigilance, cleanliness, and cautiousness. By adopting these proactive measures and staying informed, you can significantly reduce the risk of encountering these unwanted pests in your home or business. If you suspect a bed bug infestation despite your preventive efforts, consult with professional pest control services to address the issue promptly and effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bed bugs are tenacious and adaptable pests that have plagued humanity for centuries. These tiny, nocturnal insects, while not known to transmit diseases, can inflict discomfort, anxiety, and economic costs on those unlucky enough to encounter them. Recognizing the signs of infestation, practicing preventive measures, and seeking professional pest control when necessary are crucial steps in managing and mitigating the impact of bed bugs. Their ability to hide, reproduce rapidly, and develop resistance to pesticides makes them a formidable adversary, requiring vigilance and informed action to keep them at bay. While the battle against bed bugs can be challenging, it is not insurmountable, and with proper knowledge and resources, infestations can be effectively controlled and eliminated, allowing for peaceful and pest-free living environments.
